Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022: A Comprehensive Review, Analysis, and Future Roadmap
The Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 emerged as one of Uttar Pradesh’s most visible employment outreach initiatives in recent years. Designed to bridge the gap between job seekers and employers, this campaign—publicized and coordinated through the official portal sewayojan.up.nic.in—aimed to aggregate vacancies, streamline recruitment, and spur inclusive economic participation across urban and rural districts. This long-form article offers an in-depth exploration of the Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022: its historical background, objectives, implementation strategy, state-level impact, measurable outcomes, success stories, bottlenecks, comparisons with other schemes, and realistic prospects for the future. The goal here is to create a thorough, SEO-optimized, and authoritative resource that helps policy analysts, students, journalists, and citizens understand what the Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 achieved—and what lessons remain.

Understanding the context: Why Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022?
Since India’s economic reforms and subsequent structural shifts, state-level employability drives have become critical tools for matching supply and demand in the labor market. Uttar Pradesh, home to a massive working-age population, faces unique structural challenges: high rural population, agrarian underemployment, migration pressures, and youth unemployment. The Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 was conceived against this backdrop to address multiple policy priorities: reducing unemployment, improving skills linkages, supporting women’s workforce participation, and encouraging local hiring to curb distress migration.
At its core, Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 sought to be more than a job fair; the initiative intended to function as a policy interface—linking training providers, employers, government departments, and aspirants through a centralized digital presence at sewayojan.up.nic.in, with on-ground mela events across districts. The initiative bundled recruitment, registration, skill mapping, and pre-placement facilitation under one programmatic umbrella.
Historical evolution of the Sewayojan portal and rojgar melas
The Sewayojan portal has served as a statewide employment exchange interface, evolving from legacy job-registries to a more dynamic online matching platform. The 2022 rojgar mela series builds on decades of public employment outreach—when employment exchanges were the primary institutional conduit—and modernizes outreach through digital registration, employer dashboards, and district-level coordination. Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 therefore sits at the intersection of old institutional memory and new digital-first policy design.
Objectives of Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022
The Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 operated with a layered set of objectives that span immediate employment, skills development, and systemic change:
Create immediate placement opportunities by bringing employers and candidates together at district melas and through the sewayojan.up.nic.in portal.
Strengthen the vocational and skilling pipeline by integrating training providers and certifying bodies into the mela ecosystem.
Promote gender-inclusive hiring through targeted outreach and incentives for women’s recruitment at local job fairs.
Reduce information asymmetry between employers and job seekers—particularly in rural areas—via digitized vacancy posting and candidate matching.
Encourage state-level coordination across departments (labor, skill development, rural development) for programmatic coherence.
These objectives reflect an attempt to address structural problems with a combination of hardware (on-ground events) and software (portal enhancements at sewayojan.up.nic.in).
Design and implementation: How Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 worked
The implementation model of Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 combined digital registration with decentralized physical melas. Key design components included:
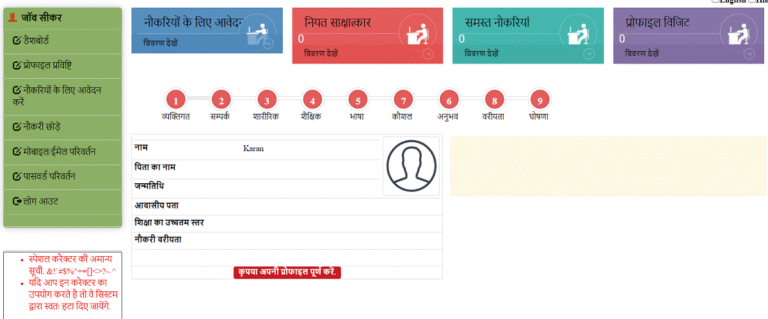
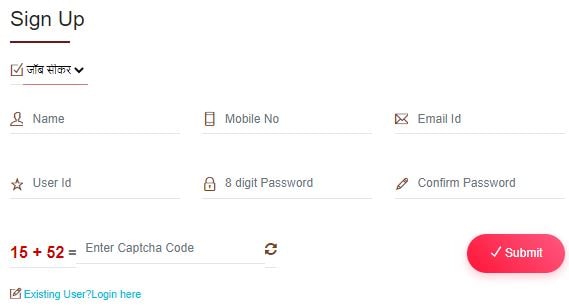
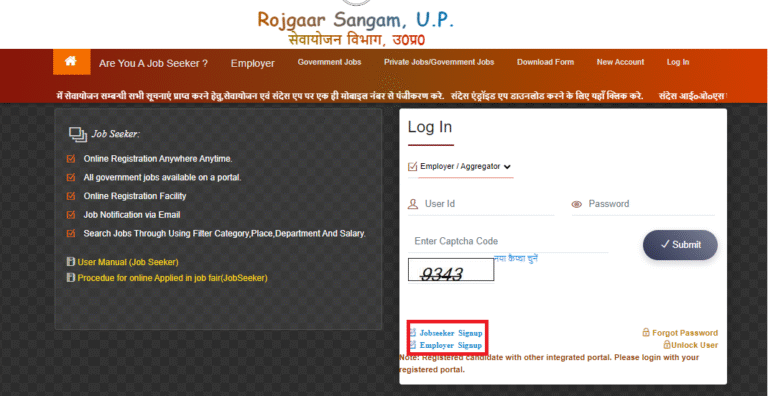
Registration and profiling: Job seekers were encouraged to register on the sewayojan.up.nic.in portal, complete a profile, upload certificates, and indicate preferences. This digital-first attempt facilitated pre-screening and rapid employer matches.
Employer engagement: Public and private employers posted vacancies on sewayojan.up.nic.in and participated in district-level melas. Sectors ranged from manufacturing and retail to government subcontracting projects.
Skill linkages: Certified training partners and vocational institutes were invited to set up stalls, offer demonstration sessions, and enroll candidates for short-term courses aligned to employer demand.
On-ground logistics: District administrations organized venue logistics, counseling booths, document verification counters, and interview halls. Priority slots were set aside for women, differently-abled candidates, and socially disadvantaged groups.
Monitoring and reporting: Post-mela placement data were collected and integrated into the sewayojan.up.nic.in dashboard to support real-time monitoring and state-level reporting.
This hybrid structure allowed Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 to reach both digitally connected youth and those who relied on local outreach for information and access.
State-level impact: Numbers, distribution, and sectors
While the scale and exact placement numbers varied by district, the Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 had a multi-dimensional impact:
Geographic distribution: Melas were organized across urban centers and rural block headquarters, ensuring reach to smaller towns. This geographic spread helped in engaging aspirants who might otherwise migrate to larger cities.
Sectoral distribution: Many placements came from labor-intensive sectors—retail, hospitality, construction, and small manufacturing units. There was also a significant chunk of contractual and project-based government employment.
Women’s participation: Targeted outreach and reserved slots raised women’s participation metrics. The mela model partnered with women’s SHGs and self-help networks to encourage female applicants.
Linkages with skill development: Short-term skilling and certificate issuance helped convert walk-in candidates into employable recruits for certain industries.
Longer-term effects: By creating direct hiring pipelines for local industries, Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 contributed to localized employment stabilization and reduced immediate migration pressures for some families.
Success stories: Real-world narratives that demonstrate impact
Success stories are the most persuasive proof of a program’s efficacy. Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 produced multiple individual and community-level successes that illustrate both the potential and the practical outcomes of well-coordinated outreach.
A young woman from a peri-urban block found a retail supervisory role after participating in a district mela listed on sewayojan.up.nic.in. The job provided regular income and a chance for on-the-job training, breaking intergenerational cycles of informal work.
A small-unit manufacturer hired a team of skilled helpers through the portal, enabling the unit to expand production. The employer credited the mela model for rapidly meeting seasonal labor demand.
Several youth received short-term training placements during the mela and were later absorbed into apprenticeships—demonstrating effective skill-to-job conversion when employers and training providers coordinate.
Municipal projects in some districts used the sewayojan.up.nic.in platform to fill contractual labor requirements, ensuring transparent hiring and timely wage payments.
These stories, while anecdotal, underscore how the Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 combined digital facilitation with human-centered outreach to produce locally meaningful outcomes.
Policy framework and institutional coordination
The Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 was embedded within a larger policy universe involving labor markets, skill development, rural livelihoods, and social welfare. Effective execution required inter-departmental coordination at the district and state levels:
Labor department: Led employer liaison, vacancy aggregation, and compliance protocols.
Skill development department: Aligned short-term training and certification to mela demand, supporting employability.
District magistrates and municipal bodies: Organized logistics, venues, and local mobilization.
Social welfare and women’s departments: Implemented targeted outreach to ensure inclusion of marginalized groups.
Integration with existing schemes: The mela platform interfaced with schemes like MGNREGA for temporary employment and state apprenticeship programs for longer-term skill absorption.
This collaborative approach underscored the need for cross-cutting policy alignment: employment solutions operate most effectively when labor, skills, and social protection are considered together.
Challenges and bottlenecks
Despite clear benefits, Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 encountered operational and structural challenges. Recognizing these hurdles helps refine future iterations.
Digital divide: While sewayojan.up.nic.in provided a digital backbone, many target beneficiaries lacked reliable internet access or digital literacy. On-ground registration counters mitigated this but increased administrative overhead.
Quality of matching: Digital profiles occasionally lacked standardization, making algorithmic matching imperfect. Employers sometimes reported receiving mismatched candidate profiles.
Sustainability of placements: Several jobs were contractual or short-term, raising concerns about long-run economic security. The model did not always convert short placements into long-term careers.
Verification and documentation: Many aspirants lacked formal certifications, complicating verification processes. This sometimes slowed hiring decisions.
Employer participation variability: While larger districts attracted a range of employers, remote districts had fewer participating firms, limiting opportunities.
Monitoring outcomes: Tracking post-placement outcomes and wages remained difficult, inhibiting robust impact evaluation.
These challenges point to the need for iterative improvements: better digital inclusion strategies, standardized profiling, stronger post-placement tracking, and incentives for employers to offer longer-term contracts.
Comparative analysis: Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 versus similar initiatives
Comparisons sharpen insight. Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 can be compared with other national and state-level employment programs to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Compared to traditional employment exchanges: The mela model is more proactive and time-bound, combining in-person hiring with digital support. Traditional exchanges often suffer from paperwork and lack of employer engagement, whereas the mela approach actively markets roles.
Compared to national mass-hiring drives: National campaigns bring scale but can lack local tailoring. Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 balanced scale with local specificity, enabling district-level customization of employer mixes.
Compared to skilling-only interventions: Pure skilling programs focus on supply-side qualifications; the mela model integrates demand-side placement. This combined approach improves immediate placement chances.
Compared to private job portals: Private platforms excel at real-time matching and scale but may lack local verification and inclusion mandates. The Sewayojan.up.nic.in platform fills that governance gap—prioritizing inclusion, verification, and public accountability.
Through these comparisons, the strength of Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 appears to be its hybrid public-digital-local approach, even while private marketplaces may outperform on pure matching efficiency.
Women empowerment and social inclusion: How the mela reached marginalized groups
A central priority of Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 was to increase women’s participation and include socially disadvantaged communities. Policy levers used included:
Reserved interview slots and priority counseling for women and differently-abled candidates.
Collaborations with women’s self-help groups to publicize melas and encourage participation.
Provision of safe interview spaces and female-only counseling booths at venues.
Encouragement for employers to commit to a minimum percentage of female hires.
Targeted skill modules for women—such as retail management, tailoring, and digital literacy—were offered at melas to create employable skillsets.
These measures improved female attendance and initial hiring, though long-term retention and career progression remained areas for further policy attention.
Economic and rural development ties
The Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 had important ties to rural development. In rural districts, the mela model influenced local economies by creating farm-nonfarm employment options, supporting small enterprises, and encouraging local value-chain development. Employers often recruited for tasks related to agri-processing, logistics, and local manufacturing—areas that can absorb rural labor and raise household incomes.
By linking local employers and job seekers, the mela reduced transactional friction and supported micro-level industrial growth. These effects contribute to broader rural development goals such as reduced migration, diversification of livelihoods, and increased household resilience.
Monitoring, evaluation, and data: Measuring outcomes
Robust monitoring and evaluation (M&E) are essential to gauge program impact. Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 included data collection features on the portal—registration counts, employer vacancies, interviews conducted, and placements made. However, effective evaluation requires longer-term tracking: wage levels, job retention, worker satisfaction, and career progression.
To strengthen M&E, future iterations should incorporate systematic follow-ups (30-day, 90-day, 6-month) and integrate payroll or social protection data where possible. Linking the portal to Aadhaar-enabled verification and welfare databases—while respecting privacy and consent—would help validate outcomes and minimize ghost entries.
Policy recommendations: Improving future melas
Based on the Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 experience, the following recommendations can improve future implementation:
Enhance digital inclusion: Deploy mobile kiosks and local digital literacy drives so sewayojan.up.nic.in functions effectively as a universal platform.
Standardize candidate profiles: Use skill tags and competency-based descriptors to improve matching quality.
Incentivize long-term hiring: Provide wage subsidies or tax benefits for employers converting temporary hires into permanent staff.
Strengthen employer outreach in remote districts: Set up industry consortiums and partner with regional chambers to diversify employer participation.
Improve post-placement tracking: Implement scheduled follow-ups and tie placements to skilling assessments.
Integrate social protection: Link short-term placements to portability of benefits and grievance redressal.
If implemented, these measures will make the portal and mela model more resilient, inclusive, and outcome-focused.
Technology and innovation: Role of sewayojan.up.nic.in
Technology is central to scaling impact. The sewayojan.up.nic.in portal served as a single-window interface for registration, vacancy posting, and monitoring during the 2022 events. To maximize technology’s potential:
Introduce AI-driven matching to surface the best candidate-employer pairs while maintaining transparency.
Offer multilingual support to cater to non-Hindi/Urdu speakers.
Provide mobile-first interfaces and low-data modes for rural users.
Build dashboards for local administrators to track real-time event metrics and resource needs.
Use data analytics to forecast sectoral demand and pre-position training programs.
These technology-driven interventions will enhance the effectiveness of future Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela instances.
Financial and budgetary considerations
Costing a multi-district rojgar mela requires line items for logistics, staffing, digital infrastructure, training, and outreach. While on-ground melas cost money, the potential economic returns—through increased employment, tax revenues, and reduced welfare burdens—can justify initial outlays. Future policy planning should account for cost-sharing models, involving central funds, state budgets, and employer contributions.
Governance and transparency
Transparency is a core strength of public platforms. Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 emphasized documented vacancy postings, documented selection criteria, and public dashboards. Strengthening transparency further—by publishing placement data by district and sector and inviting third-party evaluations—will build public trust and make corrective actions easier to implement.
Scalability and sustainability
For Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 to evolve into a sustainable instrument, it must move from episodic events to continuous market-making operations. This requires:
Regular small-scale melas with local industries.
Sustained employer engagement strategies.
Continuous upskilling pipelines that feed directly into employer demand.
Policy mechanisms that convert temporary jobs into durable employment paths.
Sustaining the model will require both institutional commitment and flexible financing.
International perspectives and lessons learned
Globally, public job fairs and digital labor-market platforms have mixed outcomes—success depends on local labor-market structures and administrative capacity. Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 aligns with international best practices by combining digital tools with human facilitation, emphasizing inclusion, and coordinating across departments. Learning from models in other federal democracies—such as targeted sectoral job drives and demand-driven skilling—can further improve local adaptations.
Looking ahead: Future prospects for Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela
The future of Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela looks promising if policymakers commit to iterative improvements. Key future prospects include:
Sectoral deep dives: Organizing industry-specific melas—textiles, agro-processing, construction—will allow for precise skilling and matching.
Gig economy interfaces: Expanding the portal to support gig worker registration and micro-task marketplaces can create new income streams for rural youth.
Apprenticeship and career pathways: Strengthening linkages with apprenticeship schemes will transform entry-level placements into career trajectories.
Local entrepreneurship: Use melas to promote micro-enterprise opportunities and local value chains, thereby increasing self-employment avenues.
In short, the sewayojan.up.nic.in platform combined with localized melas can form the backbone of a dynamic, inclusive state-level employment ecosystem.
Practical guidance for job seekers and employers
For job seekers: Register comprehensively on sewayojan.up.nic.in, maintain accurate skill records, carry scanned documents to on-ground melas, attend counseling booths, and pursue short-term certifications where suggested. Engage proactively with follow-up mechanisms and understand terms of employment (contract length, wages, social protection coverage).
For employers: Use sewayojan.up.nic.in to standardize vacancy postings, request pre-screened candidate lists, participate in local melas to meet candidates face-to-face, and consider offering probation-to-permanent pathways to improve retention.
These simple operational practices will make the mela experience more productive for all stakeholders.
Measuring success: What counts?
Success metrics for Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 include not just raw placement numbers but also qualitative outcomes:
Placement rate: Percentage of attendees who secured offers.
Retention rate: Proportion of hires still employed after 3–6 months.
Wage benchmarks: Comparison of wages against regional standards.
Skill certification: Number of candidates who obtained recognized certificates.
Inclusion metrics: Participation rates for women, SC/ST, and differently-abled candidates.
Employer satisfaction: Surveys to gauge employer experience with the portal and melas.
When these metrics are aggregated and published, they will create an evidence base that enables continuous improvement.
Challenges to anticipate and mitigate
As the model evolves, several challenges must be proactively addressed:
Quality assurance of training providers.
Avoiding short-termism that prioritizes any placement over sustainable livelihoods.
Ensuring data privacy and consent in portal operations.
Balancing digital scalability with human facilitation for vulnerable groups.
These challenges require governance frameworks, standard operating procedures, and stakeholder consultations.
Conclusion: Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 in retrospect
The Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 represented a significant push by the state to upgrade employment outreach. By combining a centralized portal with district-level melas, the initiative sought to overcome information gaps, mobilize local employers, and support vulnerable job seekers. The program delivered measurable placements, enhanced female participation, and created linkages between skilling and hiring—yet it also revealed gaps around digital inclusion, long-term job security, and data-driven monitoring.
Moving forward, the sewayojan.up.nic.in platform—if continuously improved—can be the linchpin of a resilient, inclusive labor-market strategy for Uttar Pradesh. Policymakers, employers, training partners, and civil society should collaborate to institutionalize best practices, scale successful local models, and convert episodic melas into a continuous, demand-driven employment ecosystem.
Frequently asked questions
What was the main purpose of Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022?
The primary goal of Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022 was to connect job seekers with employers through a combined digital registration platform and district-level job fairs, aiming to create immediate employment opportunities, foster skill linkages, and promote inclusive hiring across Uttar Pradesh.
How did sewayojan.up.nic.in support candidates during the 2022 melas?
The sewayojan.up.nic.in portal facilitated online registration, candidate profiling, vacancy viewing, and preliminary matching. On the ground, melas provided counseling booths, document verification, and pre-placement interviews to assist candidates lacking digital access.
Were there specific provisions for women and disadvantaged groups in Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela 2022?
Yes. The program included targeted outreach, reserved interview slots, female-only counseling spaces, partnerships with SHGs, and training modules aimed at increasing women’s participation and supporting marginalized social groups.
Did the 2022 rojgar melas lead to long-term jobs?
Outcomes were mixed. Many placements were immediate and contractual, providing short-term income. Some melas resulted in longer-term hires and apprenticeships, but converting temporary roles into permanent, sustainable employment remains a policy focus.
How can employers participate in future Sewayojan.up.nic.in melas?
Employers can register on sewayojan.up.nic.in, post vacancies, request pre-screened candidate lists, and participate in district melas. They are encouraged to collaborate with local authorities for mass hiring and consider mechanisms for longer-term retention.
What are key improvements suggested for future Sewayojan.up.nic.in Rojgar Mela initiatives?
Recommendations include enhancing digital inclusion (mobile kiosks, multilingual support), standardizing candidate profiles, incentivizing permanent hiring, strengthening post-placement tracking, and improving employer outreach in remote districts.
Where can I find more official information about the Sewayojan portal and rojgar melas?
Official updates, registration portals, and employer resources are available at the sewayojan.up.nic.in website.