Sewayojan Registration: A Complete Guide to Accessing Employment, Skills, and Social Benefits
Sewayojan registration has become a cornerstone for job seekers, entrepreneurs, and community organizations aiming to access employment opportunities, government-led skill programs, and targeted welfare schemes. Whether you are a recent graduate seeking your first job, a woman entrepreneur looking for support, or a rural youth hoping to join a local skill training initiative, completing your sewayojan registration opens doors to curated vacancies, career counseling, and state-specific benefits. This article explains everything about sewayojan registration—history, objectives, how it works, state-level implementation, real-world success stories, challenges, comparisons with similar mechanisms, and the roadmap ahead—so you can act confidently and make the most of the system.
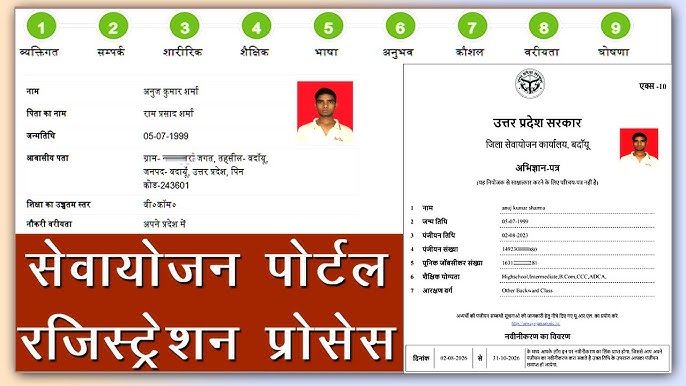
Why Sewayojan Registration Matters
Sewayojan registration is more than an online form. It is the digital handshake between citizens and state employment ecosystems. The registration creates a verified profile that allows government employment exchanges and related portals to match job seekers with vacancies, invite them to rojgar melas (job fairs), route them to skill-development programs, and make them eligible for targeted assistance such as women empowerment initiatives or rural livelihood support.
For policy-makers, sewayojan registration produces structured data that helps plan local training, identify skill shortages, and design social welfare initiatives. For employers—public and private—the registered database simplifies recruitment and shortlists candidates with verified credentials. The result is a more transparent, efficient, and measurable path from unemployment or underemployment to sustainable livelihoods.
Brief History and Policy Background
Employment exchange systems in India have long roots—growing from localized employment offices to modern digital platforms. Sewayojan registration, in many states, is the contemporary evolution of these exchanges. Historically established employment registries have progressively been modernized to become state-run portals like the Sewayojan portal, integrating registration, job matching, skill mapping, and placement services under one user-centric interface. The digitization objective has been to reduce manual paperwork, increase reach into rural areas via Common Service Centers (CSCs), and improve the targeting of schemes aimed at marginalized groups.
The Uttar Pradesh Rojgaar Sangam / Sewayojan portal is a primary example: established to centralize employment exchange services and connect job seekers, employers, and training providers through a single interface. This portal allows registration for job seekers and employers, lists government and private vacancies, and supports recruitment drives such as rojgar melas.
Objectives of Sewayojan Registration
The core objectives of sewayojan registration include:
-
Creating a verified database of job seekers to facilitate accurate job matching.
-
Enabling online applications for government and private sector vacancies.
-
Supporting targeted schemes—such as women empowerment, youth skill vouchers, and rural employment linkages—by identifying eligible beneficiaries.
-
Harmonizing placement drives, career counseling, and training pathways.
-
Providing transparency and accountability in the delivery of employment and welfare programs.
By completing sewayojan registration, individuals get proactive notifications about suitable jobs, invitations to recruitment events, and information on eligibility for livelihood-related schemes.
Who Should Register?
Sewayojan registration is typically open to:
-
Recent graduates and unemployed youth.
-
Women seeking employment or self-employment support.
-
Persons with disabilities seeking specialized placement services.
-
Employers and industry recruiters who want to post vacancies.
-
NGOs, training organizations, and placement agencies coordinating schemes.
-
Government officers and district administrators managing local employment drives.
Because the portal functions as both an employment register and a platform for scheme delivery, registration helps a wide cross-section of citizens engage with state programs and private hiring.
Step-by-Step: How Sewayojan Registration Works
The exact layout and field names may vary slightly across states, but the registration flow follows common steps. The following is a practical walkthrough tailored to a typical sewayojan registration process:
-
Access the Official Portal
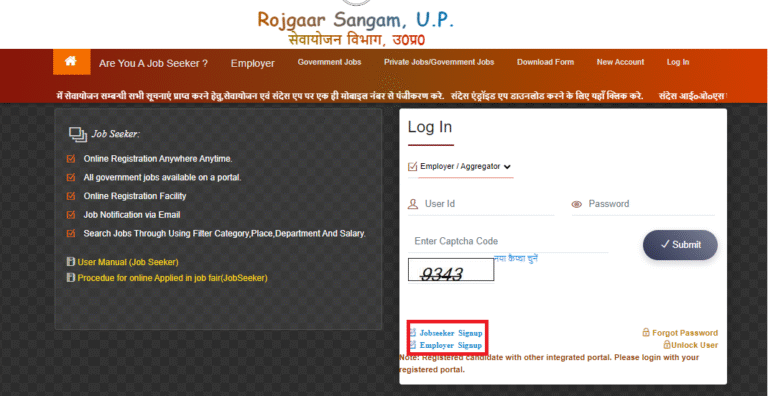
Visit the official Sewayojan portal of your state or the centralized link for your employment exchange. For Uttar Pradesh and similar state-level portals, the official domain and registration pages are publicly available. Always confirm you are on the government domain before entering sensitive data. -
Choose Your User Type
Select whether you are a job seeker, employer, training provider, or government officer. The user type determines the fields in the registration form and the services you can access. -
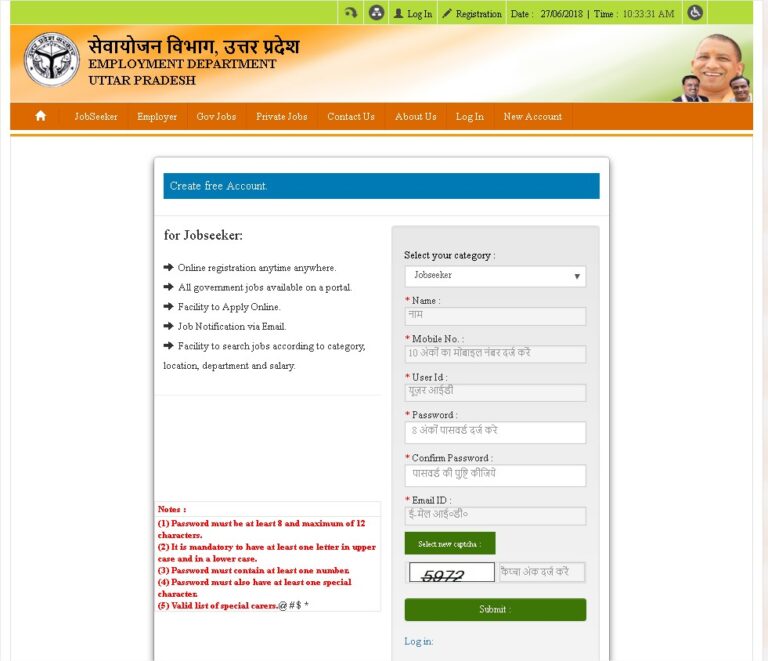
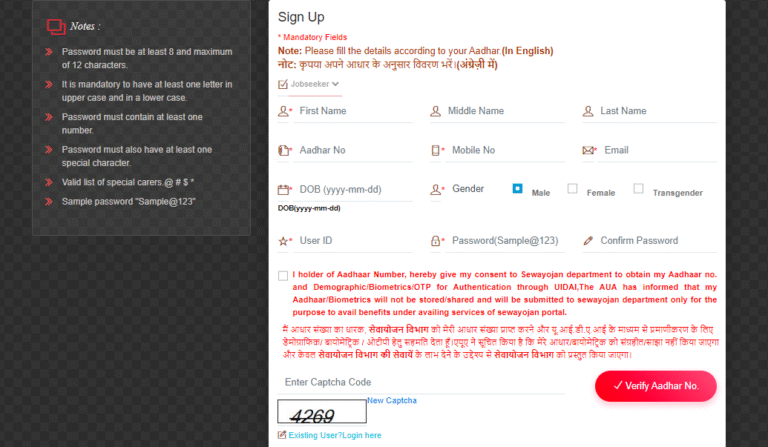
Provide Basic Personal Details
Enter name, date of birth, gender, contact mobile number, email address, and full residential address. Many portals require Aadhaar/identity verification for authenticity. -
Educational and Professional Information
Add details of highest qualification, institution, year of passing, and special skills or trades. If you have prior job experience, list roles and employers. -
Upload Documents
Most registrations need scanned copies or photographs of identity proof (Aadhaar or voter ID), photographs, educational certificates, and bank account details for scheme disbursals. -
Select Job Preferences and Locations
Choose preferred job categories (government/private), salary range, job type (full-time/part-time), and preferred districts or urban centers. -
Submit and Verify
Review, submit, and complete any OTP or Aadhaar-based verification steps. Keep your login credentials secure. -
Profile Activation and Follow-Up
After successful sewayojan registration, use your login to track job notifications, apply to listed positions, and accept invitations for rojgar melas or training sessions.
Several state district sites and guidance pages provide local instructions to help with sewayojan registration and post-registration services.
Documents and Practical Tips for Successful Registration
To ensure smooth sewayojan registration, prepare the following:
-
Aadhaar card (or other government ID).
-
Passport-size photograph in digital format.
-
Educational certificates and mark sheets.
-
Caste or income certificate if claiming quotas or scheme-specific benefits.
-
Bank account details (for stipend or benefit transfer).
-
Active mobile number and email ID.
Practical tips: use a desktop or a reliable CSC if your internet is slow, cross-check scanned documents for legibility, and choose realistic job preferences to receive relevant notifications. If you are registering for programs targeted at women, rural populations, or persons with disabilities, ensure that you upload the specific certificates that establish eligibility.
Sewayojan Registration and State-Level Implementation
Sewayojan registration is implemented across states with necessary adaptations. While the central idea is uniform—register job seekers and link them to employment and skill programs—states customize modules for local priorities:
-
Uttar Pradesh: The Sewayojan / Rojgaar Sangam portal coordinates large-scale placement drives, rojgar melas, and state-specific skill initiatives. The portal also enables district employment offices to manage data and invite candidates for interviews.
-
District-Level Adaptations: Many district websites link directly to the sewayojan registration page and provide localized support points, such as the Ghaziabad and Varanasi district employment offices, where citizens can get assistance or register offline through CSCs.
-
Language and Accessibility: Portals increasingly provide multilingual support and simple UI features so rural users and less digitally literate applicants can complete sewayojan registration with help from CSC operators.
These state-level variations require applicants to check their local employment office or district website for exact forms and documents tied to sewayojan registration.
Sewayojan Registration: Connecting to Women Empowerment & Rural Development
One of the strengths of the sewayojan registration framework is its ability to integrate targeted schemes. For example, when a woman completes sewayojan registration, her profile becomes visible to programs focused on women entrepreneur grants, self-help group (SHG) linkages, and short-term skill courses geared toward female-led micro-enterprises. Similarly, rural job seekers who register can receive notifications about agriculture-related roles, rural public works, or skill training adapted for local economies.
This integration ensures that sewayojan registration is not merely about urban white-collar jobs; it also channels rural residents into appropriate livelihoods and social welfare initiatives.
Practical Use-Cases and Success Stories
Across states, sewayojan registration has produced measurable successes. Here are representative scenarios:
-
Mass Placement Drives: Rojgar melas organized using the sewayojan database resulted in bulk hiring for roles in retail, manufacturing, and government contractual positions. Employers prefer the portal because it shortlists vetted candidates quickly.
-
Women’s Self-Employment: After sewayojan registration, many women were routed to short entrepreneurial training programs and microcredit options, enabling them to start small enterprises—from tailoring units to agri-linked micro-enterprises.
-
Rural Skill Matching: In rural districts, sewayojan registration helped map local skill sets (agriculture, animal husbandry, trades), enabling targeted training that led to higher placement and improved incomes.
-
Reducing Vacancy Mismatch: Employers who register vacancies on the portal report reduced hiring time because matched applicants from sewayojan registration profiles are better aligned with job requirements.
These examples are representative of the portal’s capacity to transform local employment dynamics when supported by committed district administration and engaged employers.
Common Challenges and Roadblocks
Sewayojan registration and portal use face several practical challenges:
-
Digital Divide: Some applicants in remote areas lack internet access or digital literacy to complete sewayojan registration online without assistance. Local CSCs mitigate this but need scale.
-
Data Quality and Verification: Incomplete or inaccurate profiles reduce the effectiveness of job matching. Offline verification processes must be robust to ensure trust.
-
Awareness Gaps: Many eligible citizens remain unaware of the benefits unlocked by sewayojan registration, especially older workers and marginalized groups.
-
Integration with National Schemes: Aligning state portals with central schemes (and vice versa) sometimes faces interoperability and administrative coordination hurdles.
-
Employer Adoption: Private employers may still prefer legacy hiring methods; greater outreach and reliability assurances are needed to attract more private-sector vacancies into sewayojan workflows.
Addressing these challenges requires consistent outreach, digital literacy drives, improved verification processes, and stronger public-private partnerships to make sewayojan registration more effective.
Comparative View: Sewayojan Registration vs Other Employment Platforms
It’s useful to contrast sewayojan registration with other digital employment solutions.
-
Sewayojan vs National Job Portals: Sewayojan often focuses on state-level vacancies and locally relevant schemes, while national portals may concentrate on broader opportunities like central government openings or large corporate recruitment. Sewayojan registration is therefore more tailored to district-level interventions and rojgar melas.
-
Sewayojan vs Private Job Platforms: Private job portals excel at white-collar and urban roles but may lack integration with government schemes and social welfare targeting. Sewayojan registration bridges the public-sector welfare benefits with placement services, which private platforms cannot offer.
-
Sewayojan vs Traditional Employment Exchanges: Digital sewayojan registration modernizes legacy employment exchanges by enabling online verification, automated matching, and integrated notifications.
Overall, sewayojan registration’s advantage is its policy alignment with state welfare priorities, local job markets, and scheme eligibility—making it uniquely positioned for inclusive employment outcomes.
How Employers and Training Providers Use Sewayojan Registration
Employers and training organizations register on the portal to post vacancies, list training programs, and identify candidates. For employers, the benefits of sewayojan registration include access to pre-verified profiles, easier outreach for hiring events, and the ability to coordinate with district employment offices. Training providers use the portal to target eligible beneficiaries—especially for state-sponsored upskilling that comes with stipends or placement commitments.
Employers should keep vacancy descriptions accurate and engage proactively in rojgar melas to build trust with the sewayojan database and recruit the best-suited candidates.
Metrics and Monitoring: What Good Outcomes Look Like
Success indicators for sewayojan registration and related programs include:
-
Increase in registered active profiles with complete documentation.
-
Number of placements through portal-matched applications.
-
Reduction in average days-to-hire for registered vacancies.
-
Percentage of women, rural residents, and persons with disabilities placed via the portal.
-
Conversion rates from short-term training to sustained employment.
Districts typically track these metrics and adjust operations—such as scheduling targeted rojgar melas or running awareness campaigns—based on the sewayojan registration data.
Policy Recommendations to Improve Sewayojan Registration Impact
To scale the benefits of sewayojan registration, states and districts can consider the following policy steps:
-
Expand Assisted Registration: Strengthen the network of CSCs and local employment offices to help digitally marginalized citizens complete sewayojan registration.
-
Standardize Interoperability: Ensure state sewayojan systems communicate with national employment and welfare platforms for smooth benefits delivery.
-
Build Employer Incentives: Offer incentives for private employers to post vacancies on the portal and to attend rojgar melas.
-
Focus on Data Quality: Periodic profile audits and simple re-verification mechanisms can maintain trust in sewayojan registration data.
-
Localized Outreach Campaigns: Use radio, local governance bodies (panchayats), and schools to increase awareness about sewayojan registration benefits.
-
Targeted Women’s Programs: Expand scheme linkages for registered women—such as seed grants, mentorship, and SHG formalization.
With these steps, sewayojan registration can be better leveraged to drive inclusive employment outcomes.
Technology & User Experience: Making Sewayojan Registration Easier
To increase adoption and reduce friction in sewayojan registration, the portal UX should follow these best practices:
-
Minimal fields for initial signup, with optional extended profile sections later.
-
Clear, multilingual guidance and video walkthroughs for each step.
-
Offline form submission options through CSCs for citizens without internet access.
-
Mobile-first responsive design and lightweight pages for low-bandwidth contexts.
-
Secure authentication and easy password recovery for returning users.
These improvements will result in higher completion rates for sewayojan registration and better-quality data for job matching.
Future Prospects: Where Sewayojan Registration Can Go Next
Looking ahead, sewayojan registration can evolve into a national employment backbone that integrates:
-
AI-powered matching for better job-fit recommendations.
-
Portable digital credentials for skills and course completion.
-
Real-time labor market analytics to guide local training programs.
-
Deeper integration with entrepreneurship and microcredit mechanisms for self-employment pathways.
-
Inclusive accessibility features such as voice-based registration and support for local dialects.
If implemented responsibly, this next phase could significantly reduce structural unemployment and accelerate inclusive economic participation.
One Official Link to Start Your Sewayojan Registration
If you are ready to register, start with the official Sewayojan portal relevant to your state—many districts and state employment services link to the official sewayojan site where you can begin the sewayojan registration process. For example, the Uttar Pradesh Sewayojan (Rojgaar Sangam) portal offers registration and login interfaces for job seekers and employers.
Real-World Checklist: After You Complete Sewayojan Registration
-
Save your login credentials securely and note the registered email/mobile.
-
Complete your profile fully—partial profiles get fewer matches.
-
Upload legible documents and verify them where the portal allows.
-
Select realistic job categories and location preferences.
-
Regularly check the portal for messages and invites to rojgar melas.
-
Attend local training programs suggested through your profile.
-
Keep documents updated (address, contact, qualifications) to preserve eligibility.
Following these steps after sewayojan registration increases the likelihood of timely job matches and benefit access.
Case Study Snapshot: District-Level Transformation
In several districts where sewayojan registration uptake was actively promoted, district administrations reported:
-
Higher participation in rojgar melas due to targeted invites based on sewayojan registration profiles.
-
Better employer-candidate matching, reducing interview no-shows and improving hiring efficiency.
-
Increased enrollments in women’s vocational programs, with higher conversion to micro-enterprise activity.
These district-level wins show that sewayojan registration, when combined with proactive local administration, can change employment trajectories for many citizens.
Addressing Misconceptions about Sewayojan Registration
-
Myth: Sewayojan registration is only for urban jobs.
Reality: The portal connects rural employment, agriculture-linked roles, skill training, and local government vacancies in addition to urban opportunities. -
Myth: Registration guarantees a government job.
Reality: Registration increases visibility and eligibility for opportunities but does not guarantee placement; training, interview performance, and vacancy-fit all matter. -
Myth: Private employers don’t use sewayojan.
Reality: Increasing numbers of private employers and training providers post vacancies and attend rojgar melas when they see the benefit of vetted candidate lists.
Clarifying these points helps applicants approach sewayojan registration with realistic expectations and proactive follow-through.
How NGOs and Community Groups Can Leverage Sewayojan Registration
NGOs and community-based organizations can use sewayojan registration to:
-
Identify eligible beneficiaries for livelihood projects.
-
Organize group registrations and verification drives.
-
Use portal data to design skill-training modules relevant to local needs.
-
Partner with district offices to host rojgar melas and placement drives.
This multi-stakeholder approach strengthens outcomes for both individuals and community programs.
Measuring Impact: What Citizens Should Expect After Registration
After completing sewayojan registration, citizens should expect:
-
Periodic job alerts and invitations for local recruitment drives.
-
Eligibility information for targeted schemes (especially for women and rural beneficiaries).
-
Opportunities to enroll in government-supported training linked to placement commitments.
-
Improved visibility to employers who use the portal for recruitment.
If you do not see expected notifications, verify your contact details and profile completeness, and reach out to your district employment office for assistance.
FAQs
Q: What is sewayojan registration and who operates it?
A: Sewayojan registration is the process of creating a verified profile on a state employment portal (often called Sewayojan or Rojgaar Sangam) so job seekers, employers, and training providers can access and post vacancies, attend rojgar melas, and participate in state-led skill and welfare schemes. It is typically operated by state employment departments and district employment offices. Sewayojan+1
Q: How do I start sewayojan registration?
A: Visit the official Sewayojan portal for your state and locate the “Registration / Sign Up” link for job seekers. Have your Aadhaar, educational certificates, passport-size photo, and bank details ready. If you’re unsure, visit a local CSC or district employment office for assisted registration.
Q: What documents are required for sewayojan registration?
A: Commonly required documents include Aadhaar or government ID, recent photograph, educational certificates, caste/income certificate if claiming quotas, and bank account details for benefit disbursal. Specific requirements vary by state.
Q: Is sewayojan registration free, and does it guarantee a job?
A: Registration is free. It does not guarantee a job but increases visibility to employers, makes you eligible for training and placement events, and links you to targeted welfare programs.
Q: Can employers post jobs on the Sewayojan portal?
A: Yes. Employers and training providers can register and post vacancies or training programs to connect with registered candidates through the portal.
Q: What if I don’t have internet access to complete sewayojan registration?
A: Visit a Common Service Center (CSC) or your district employment office for assisted registration—a common option provided across districts to reduce the digital divide.
Q: Where can I get official help or the portal link for sewayojan registration?
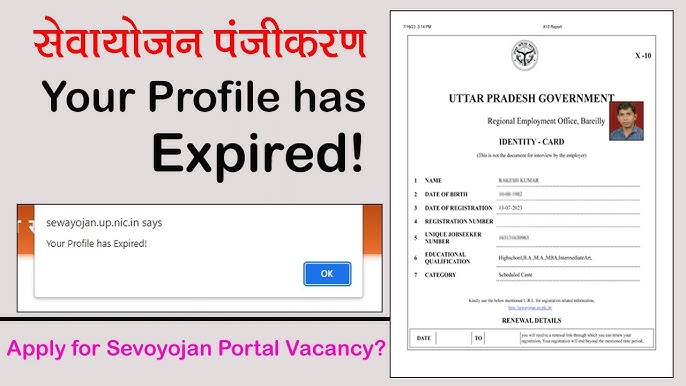
A: Start with your state employment department website or the district employment office. For Uttar Pradesh, for example, visit https://sewayojan.up.nic.in. Always use official government domains for secure sewayojan registration. Sewayojan+1
Sewayojan registration is both a practical step for individual jobseekers and a strategic policy tool for states aiming to reduce unemployment and strengthen livelihoods. By ensuring that registration is accessible, verified, and linked to concrete training and placement outcomes, governments and citizens can together turn digital registration into real economic opportunity. If you’re ready to take the next step, prepare your documents and begin your sewayojan registration on your state portal—your profile may be the connection between today’s search and tomorrow’s stable livelihood.