Sewayojan UP NIC in Registration: Complete Guide, Impact, Challenges and Future Prospects
Sewayojan UP NIC in registration is the digital doorway for millions of job-seekers, employers, and government departments across Uttar Pradesh who want to connect, apply, and recruit through a state-managed employment platform. Launched and maintained on the official domain sewayojan.up.nic.in, the portal—often referred to as Rojgaar Sangam or Sewayojan—centralizes job listings, employer vacancies, skill records, and candidate profiles so that opportunities reach the right people efficiently. This article provides a deep, authoritative, and actionable exploration of sewayojan up nic in registration: its history, objectives, how registration works step-by-step, state-level impact, success stories, operational challenges, comparisons with similar schemes, and future prospects. Throughout, we also examine how the portal aligns with broader policy frameworks such as rural development, women’s empowerment schemes, and social welfare initiatives. For concreteness on official features and registration mechanics, refer to the Sewayojan official portal pages and registration resources.
Why Sewayojan UP NIC in Registration Matters
Sewayojan up nic in registration transforms the traditional model of walk-in registrations and paper-based employment exchanges into an inclusive, searchable, and verifiable online registry. For a state as populous and economically diverse as Uttar Pradesh, having a central digital employment ecosystem removes geographical friction, enables faster matching of vacancies with candidates’ skills, and supports government efforts to reduce unemployment and underemployment at scale. The portal also integrates with Aadhaar-based verification and provides job alerts, vacancy tracking, and employer dashboards—features that significantly modernize labor market intermediation in the state.
A Short History of Sewayojan and the Digital Transition
Employment exchanges in India have a long history as intermediaries connecting job-seekers to vacancies. Over time, the need to modernize these services became apparent—manual registers, slow vacancy dissemination, and limited outreach hindered matching and timely access. Uttar Pradesh responded by digitizing its employment exchange services through the Sewayojan platform hosted on the NIC domain, introducing sewayojan up nic in registration as the primary mechanism for job-seeker onboarding. The portal is an evolution—rebranding from older employment exchange systems to a modern portal that supports job-seeker registration, employer postings, and cross-departmental coordination. Official documentation and portal pages outline the steps for job-seeker sign-up and employer registration, confirming that the state aims to bring every registered candidate online and within reach of recruiters.
Core Objectives of the Sewayojan Initiative
Sewayojan up nic in registration serves several interconnected objectives:
To create a reliable digital registry of job-seekers in Uttar Pradesh, capturing education, skills, experience, and preferences.
To streamline employer recruitment by providing dashboard tools for vacancy posting, applicant shortlisting, and communication.
To promote equitable access—especially for rural youth, women, and marginalized communities—by making registration and job alerts widely available.
To integrate with training and skilling programs so that skills gaps can be identified and addressed through targeted interventions.
To complement social welfare and rural development policies by linking beneficiaries with employment opportunities and public sector vacancies.
These objectives reflect a policy framework that seeks not only to list vacancies but to create a pipeline from registration to sustainable employment and career development.
Who Should Register and Why
Sewayojan up nic in registration is designed for a wide range of users:
Recent graduates and school-leavers looking for state-level or central government jobs.
Experienced professionals seeking transfers or new positions within Uttar Pradesh.
Rural and semi-urban job-seekers who previously depended on local employment offices.
Employers—from private enterprises to government departments—that need a verified talent pool.
NGOs and skill training bodies looking to track placements and outcomes.
Registration creates a searchable profile that employers use to filter candidates by district, qualification, category, and skill — increasing the likelihood of relevant matches and lowering search costs for both sides.
Step-by-Step: How Sewayojan UP NIC in Registration Works
The sewayojan up nic in registration process is intentionally structured to be user-friendly while capturing sufficient detail for meaningful matches. Below is a practical walkthrough based on the portal’s registration pages and official guidance.
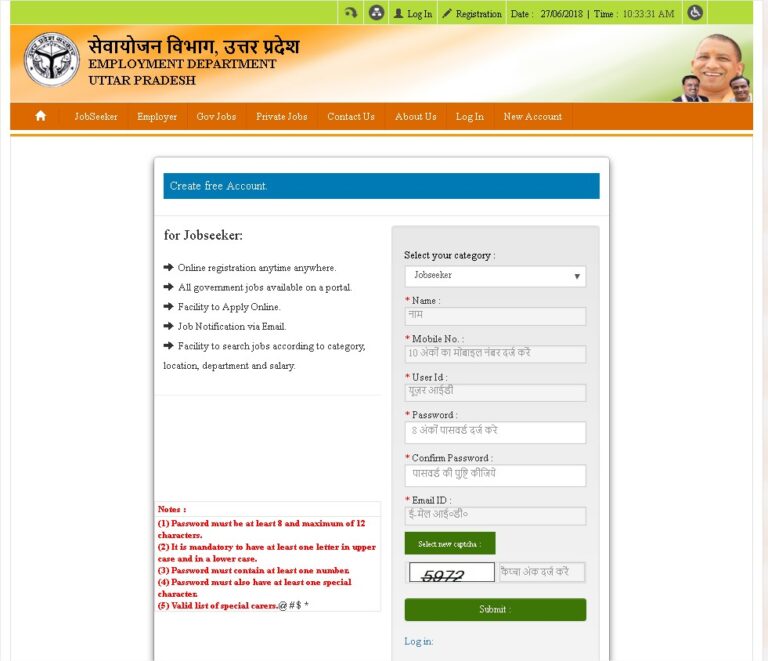
Access the portal: Visit the Sewayojan official site on the NIC domain and choose the job-seeker sign-up or “Make Free Account” option on the registration page.
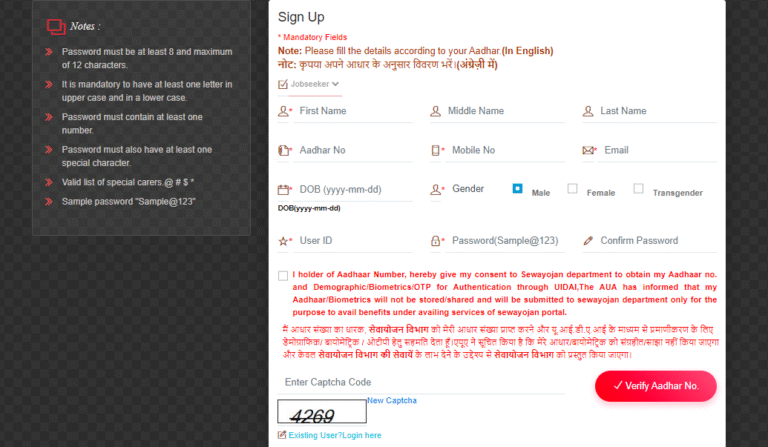
Basic personal details: Enter full name, date of birth, gender, and father/mother’s name. Provide a valid mobile number and email address for OTP verification. A user-id and password are created at this stage.
Aadhaar verification: To verify identity and prevent duplications, users are required to verify Aadhaar—this step helps ensure authenticity and allows integration with other government databases. The portal provides a “Verify Aadhaar No.” function as part of registration.
Contact and address: Provide permanent and current address details—state, district, tehsil/village, and pin code. This helps align candidates with district-specific vacancies and rural development initiatives.
Educational and skill profile: Add academic qualifications, vocational training, certifications, and language proficiencies. The portal captures whether a candidate can speak, read, or write specific languages—a useful filter for roles requiring local language skills.
Employment preferences and experience: Declare job preferences—sector, salary expectations, willingness to relocate, and area of work—as well as past work experience and professional summaries.
Physical and demographic details: Fields such as height, weight, blood group, and disability status (if any) are included, which is often necessary for specific government recruitment categories or welfare-linked placements.
Declaration and printout: Candidates submit a declaration and can print a registration report (for instance, the X-10 Report) to keep a hard copy for records. sewayojanportal.com
Post-registration features: After sewayojan up nic in registration, candidates receive job notifications via SMS and email for matches. They can log in with their user-id and password, update profiles, apply for vacancies, and access employer communications.
This step-by-step design ensures a robust profile while keeping the user experience straightforward. For employers, a parallel employer registration flow allows vacancy uploads and candidate shortlisting through the portal’s active dashboard.
Technical and User Support Features
Sewayojan provides logistical support like helpdesk contacts, FAQs, and login assistance. If a user forgets their password, the portal has a “Password/User ID Forgot” option which uses mobile-based OTP verification for recovery. District employment offices often assist users who need in-person help or lack internet access, aligning the digital portal with physical outreach. Official portal documentation lists the process for password recovery, support email contacts, and local office assistance. Sewayojan+1
State-Level Impact: How Registration Translates to Outcomes
Sewayojan up nic in registration aims to produce measurable outcomes across multiple state priorities:
Urban and rural employment matching: By capturing district-level residence and job preferences, the portal supports targeted placements in rural development projects and urban private-sector roles.
Women’s workforce participation: The registration process can identify women who are ready for employment and redirect them to women-centric schemes, trainings, and government vacancies—helping close gender gaps in the labour force.
Social welfare synergy: Candidates who are beneficiaries of income support or skill development programs can be tracked and offered employment opportunities that align with their training.
Policy feedback loop: Aggregated registration data allow policymakers to see skills shortages by region or sector, enabling targeted skilling programs and fiscal interventions.
Case studies in some districts show improved employer reach and faster filling of vacancies—particularly for contractual and outsourced positions where employers value walkthroughs of candidate profiles on the portal.
Real-Life Success Stories and Use Cases
The most compelling evidence of impact comes from individual and local success stories: a young graduate from a rural tehsil who, after sewayojan up nic in registration and a local skilling workshop, received targeted job alerts and secured a clerical role in a public body; a women’s self-help group whose members registered and accessed short-term vocational programs, leading to placement in catering and tailoring contracts; and small towns where employers use the portal to find technicians and mid-level staff that previously required long recruitment cycles. These examples underline how registration—when combined with local facilitation—bridges talent with opportunity.
Integration with Skill Programs and Employment Fairs
Sewayojan up nic in registration is designed to be more than a static repository. The portal frequently lists employment mela (job fair) vacancies and links trained candidates with recruiters at district-level events. This integration accelerates the final placement step by combining online pre-screening with offline interviews—a hybrid model that preserves the human touch while leveraging digital reach.
Challenges and Limitations
No large-scale digital employment system is without challenges. Sewayojan faces operational and structural bottlenecks that require attention:
Digital divide: While many urban and semi-urban users register easily, rural candidates without smartphones or literacy support may struggle. District facilitation centers and sewa mitras help, but coverage is uneven.
Data accuracy and updating: Profiles require regular updates to stay relevant. Many users register once and do not maintain active profiles, limiting match quality.
Matching quality: Automated match algorithms depend on complete profiles. When educational or skill fields are incomplete, candidate visibility drops.
Employer adoption: While many government departments use the portal, some private employers still prefer traditional hiring channels. Increasing employer buy-in is essential for greater demand-side depth.
Fraud and impersonation: Aadhaar verification helps, but vigilance is required to prevent fake postings or phishing attempts that exploit job-seekers’ aspirations.
Acknowledging these bottlenecks is the first step toward policy remedies—mobile camps, simplified update flows, employer outreach drives, and stronger verification protocols can reduce friction.
Comparing Sewayojan with Other State Portals and National Platforms
Sewayojan up nic in registration sits among a landscape of employment portals: national platforms like the National Career Service (NCS), state employment portals in other large states, private job portals, and skill-platform integrations. Key comparative insights include:
Depth vs breadth: National platforms have broader reach but may lack district-level specificity. Sewayojan benefits from local language interfaces and district filters that prioritize local hires.
Integration with local welfare: Sewayojan is closely aligned with Uttar Pradesh’s rural development and social welfare initiatives, which can lead to more context-sensitive placements (for example, linking MGNREGA, skilling programs, and local recruitment drives).
User experience: Some private portals offer advanced search and applicant tracking systems favored by recruiters; however, Sewayojan’s public mandate focuses on inclusion and equitable access rather than monetized premium features.
Data ownership and privacy: State portals hosted on NIC adhere to public data governance norms—this matters for users concerned about privacy and government accountability.
Where Sewayojan stands out is in its ability to aggregate state-level workforce information, feed policy planning, and support targeted social inclusion measures.
Best Practices for Job-Seekers Using Sewayojan
To maximize the benefit of sewayojan up nic in registration, candidates should adopt certain practices:
Complete the profile fully: List all qualifications, certifications, and language abilities to improve match relevance.
Keep the profile updated: Refresh employment status, experience, and preferences at least once every six months.
Use district filters: Employers often search by district; accurate address fields increase visibility.
Opt into job alerts: Turn on SMS and email notifications so you receive timely vacancy updates.
Attend local employment melas: Use online pre-screening as preparation for offline interviews offered through the platform.
Best Practices for Employers and Departments
Employers and hiring managers can increase placement success by:
Posting clear job descriptions: Specify required qualifications, experience, and location to reduce unfit applications.
Using screening filters: Leverage the portal’s filters for education, skill, and district to shortlist effectively.
Engaging with district facilitation centers: For rural hiring drives, partnership with local employment offices can smooth logistics.
Providing feedback and closure: Marking applications as reviewed or closed helps keep candidate records accurate.
Employers who adopt these practices help build trust in the portal and improve its overall efficacy.
Policy Recommendations to Strengthen Sewayojan
To amplify the positive impact of sewayojan up nic in registration, policymakers should consider:
Expanding sewa mitra coverage: More supported onboarding centers in rural blocks to help registration and profile maintenance.
Strengthening skilling linkages: Integrate the portal more tightly with training providers and outcome tracking, ensuring that registered candidates are funneled into demand-driven programs.
Employer incentives: Offer streamlined mechanisms for small and medium enterprises to post vacancies and access subsidized recruitment support.
Data-driven planning: Use aggregated portal data to design district-level employment interventions—e.g., targeted short-term trainings where supply-demand mismatches appear.
User education campaigns: Run awareness drives explaining how to register, update, and apply on sewayojan up nic in registration to boost active engagement.
Such measures will deepen the portal’s reach and its role as a policy instrument.
Measuring Success: Metrics and KPIs
To evaluate sewayojan up nic in registration, relevant performance indicators include:
Number of active registered job-seekers (monthly active users).
Vacancy fill rate: proportion of posted positions that lead to successful hires.
Time-to-hire: days between posting and appointment.
Women and marginalized group placement rates.
Geographic coverage: registrations per district relative to population.
Employer satisfaction scores.
Continuous monitoring of these KPIs—combined with qualitative user feedback—will help evolve the portal responsibly.
Technological Enhancements and Future Prospects
Looking ahead, sewayojan up nic in registration can evolve with modern features:
Mobile-first UX: A lightweight app/interface for low-bandwidth environments to widen rural access.
AI-powered matching: Use machine learning to suggest upskilling pathways and more precise vacancy matches.
Multi-lingual support: Expand local language content to reduce barriers for non-Hindi or non-English speakers.
Integration with payment and apprenticeship systems: Strengthen linkages that convert short-term placements into sustainable careers.
API interoperability: Allow approved skill providers, employers, and national platforms to exchange vacancy and candidate data securely.
These technological steps can make the portal adaptive, inclusive, and future-ready.
Addressing Equity: Women, Rural Youth, and Social Welfare
Sewayojan’s potential for social impact is strongest when it is used intentionally for inclusion. Targeted interventions that leverage sewayojan up nic in registration include:
Women-centric job alerts: Prioritize schemes and vacancies suitable for women, including flexible-hour roles, which can boost participation.
Rural micro-placement programs: Use district registration data to support local enterprises that can absorb semi-skilled labor.
Linking with social welfare: Pathways from welfare receipts to gainful employment—through training modules and guaranteed interview processes—help vulnerable groups exit dependency cycles.
When registration is combined with empowerment schemes and proactive policy, the portal becomes a means of socioeconomic transformation.
Governance, Data Privacy and User Trust
A public employment portal must be governed with transparency and care. Sewayojan—hosted under the NIC domain—follows government protocols for data handling, but ongoing vigilance is essential:
Clear privacy policies: Users should know how their data will be used and by whom.
Consent-based sharing: Information should only be shared with employers or agencies with the user’s consent.
Secure authentication: Strong OTP/Aadhaar-based checks reduce fraud risk.
Complaint redressal: A visible grievance mechanism increases user confidence.
Trust is foundational—without it, job-seekers will hesitate to use the platform meaningfully.
Implementation Lessons from the Field
Field implementations reveal practical lessons:
Combine digital registration drives with offline support: Digital-only campaigns leave gaps; hybrid models work best.
Use local champions: Sewa mitras and employment officers who understand local labor markets help close the last-mile gap between registration and placement.
Monitor inactive registrations: Outreach to dormant profiles can resuscitate candidate pools for urgent vacancies.
Employer training: Teach HR teams in SMEs how to use the portal’s filters and dashboards for efficient hiring.
These pragmatic lessons can guide scaling while preserving service quality.
How Sewayojan Compares to Private Job Marketplaces
Private job portals often offer polished interfaces and nationwide reach, but public platforms like sewayojan up nic in registration provide unique advantages:
Public accountability: Governed by state rules and oversight, the portal adheres to public-purpose goals like inclusion and nondiscrimination.
No cost barriers: Employers and candidates often access core features free of charge.
Locality focus: District-level filters and direct linkages to state schemes make Sewayojan particularly relevant for local recruitment.
Rather than seeing private and public portals as competitors, synergy—data exchanges and referrals—can create a richer ecosystem for job-matching.
Future Scenarios: From Registration to Sustainable Employment
The pathway from sewayojan up nic in registration to sustainable livelihoods depends on coordinated action:
Scale skilling to match portal demand signals.
Provide entrepreneurship modules for candid’atess who prefer self-employment.
Develop sector-specific pipelines for high-demand industries—healthcare, construction, IT, and manufacturing.
Measure long-term outcomes such as retention rates, income increases, and career progression to evaluate real impact.
In the best-case scenario, registration becomes the first step in a continuum: registration → training → placement → career growth.
Quick Practical Checklist for Registration Success
Keep Aadhaar and educational documents handy for verification.
Use clear, concise language in profiles and highlight vocational courses.
Select districts and job preferences carefully—this shapes the alerts you get.
Check the portal regularly; many vacancies are time-sensitive.
Conclusion
Sewayojan up nic in registration is a strategic instrument in Uttar Pradesh’s labour market modernization. It digitizes employment exchange functions, provides district-focused matching, and aligns with broader policy goals like rural development and women’s empowerment. While challenges such as the digital divide and employer adoption remain, smart policy action—paired with technological enhancements and local facilitation—can make the portal a decisive engine of inclusive growth. Whether you are a job-seeker, employer, or policymaker, understanding how to use sewayojan up nic in registration effectively is essential for unlocking opportunities and shaping a more resilient workforce in Uttar Pradesh. For official registration mechanics, job listings, and support, consult the Sewayojan portal and its registration pages. Sewayojan+1
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is sewayojan up nic in registration and why should I use it?
Sewayojan up nic in registration is the official online registration system on the Sewayojan portal for job-seekers in Uttar Pradesh. It helps you create a verified profile, receive vacancy alerts, apply for government and private postings listed on the portal, and track employer communications.
How do I complete sewayojan up nic in registration if I don’t have internet access?
District employment offices, sewa mitras, and local facilitation centers often assist candidates with sewayojan up nic in registration. Visit your nearest employment office for in-person help to create and verify your profile.
Which documents are required for sewayojan up nic in registration?
Typically you will need Aadhaar for verification, educational certificates, residence proof, caste or income certificates if applicable, mobile number, and an email ID. The portal’s registration page outlines specific document requirements.
How can employers use the portal after sewayojan up nic in registration?
Employers register separately to post vacancies, view shortlisted candidates, and manage communication. After employer registration, vacancies can be uploaded and matched with candidate profiles captured through sewayojan up nic in registration.
Is sewayojan up nic in registration linked to Aadhaar and is my data safe?
The portal uses Aadhaar-based verification to ensure authentic profiles. As a government-hosted platform, it adheres to public sector data handling norms—users should review the portal’s privacy statements and use secure credentials to safeguard accounts.
How often should I update my sewayojan up nic in registration profile?
To remain visible to employers and matching algorithms, update your profile whenever there is a change in qualification, experience, or job preference—at least every six months is recommended.
Can sewayojan up nic in registration help with skill development and training placements?
Yes. The portal often coordinates with skilling initiatives and employment melas; registration data can highlight local skill gaps and funnel candidates into targeted training programs that lead to placement opportunities.
For authoritative guidance, registration help, and to begin the sewayojan up nic in registration process, visit the official Sewayojan portal and the jobseeker registration page.